Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) Systems: The Future of Sustainable Energy Production
The pursuit of sustainable and eco-friendly solutions in energy production has increased interest in Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) systems. ORC is an innovative technology that operates at low temperatures and generates electricity by recovering waste heat. In this article, we will discuss how ORC systems work, their advantages, and various application areas.Video linki eklenecek;
What is the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) ?
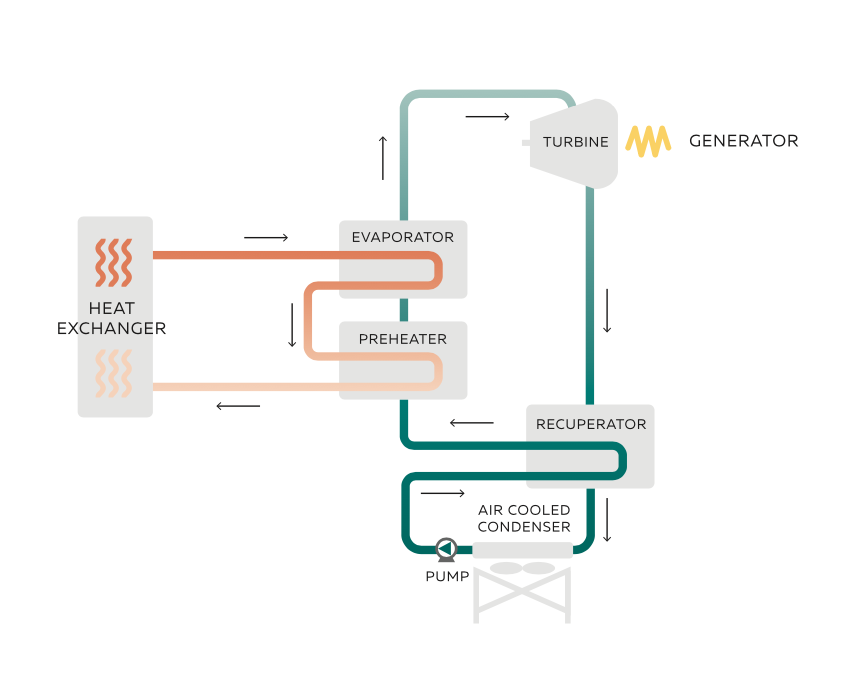
Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) is a technology where a liquid working fluid is vaporized at low temperatures, and the resulting vapor is passed through a type of turbine or expansion machine to produce electricity. This cycle is ideal for waste heat recovery, making it commonly used in industrial facilities, geothermal sources, and solar collectors.
Working Principle Of ORC Systems
Heating (Evaporation): The working fluid used in the ORC system boils at low temperatures and exhibits vaporization properties. This step is typically provided by waste heat or solar energy.
Vapor Expansion: The vaporized fluid is expanded by a turbine or expansion machine, generating mechanical energy.
Cooling (Condensation): The expanded vapor is then cooled and condensed. The heat released in this step is usually removed using cooling water or air.
Electricity Generation: The condensed fluid rotates a generator, producing electrical energy.
Advantages And Application Areas
Advantages:
Waste Heat Recovery: ORC systems stand out for their ability to efficiently utilize low-temperature waste heat generated in industrial operations and thermal energy sources.
Operation at Low Temperatures: ORC systems do not require high temperatures to operate, giving them an advantage in generating energy from low-temperature sources.
Environmentally Friendly: The working fluids used are typically environmentally friendly organic compounds, making ORC systems a sustainable option from an environmental perspective.
Application Areas:
Industrial Facilities: Used in industrial facilities to recover waste heat.
Geothermal Energy: Ideal for electricity generation using low-temperature heat from geothermal sources.
Solar Energy: Utilizes low-temperature heat collected through solar collectors.
Bioenergy Plants: Can utilize waste heat generated from bioenergy production processes.